Learning Outcomes in Listing:
i. Identify the dietary sources of Vitamins A, C, and D.
ii. Describe the metabolic functions of Vitamins A, C, and D in the human body.
Learning Outcomes Described:
Students will learn about the essential vitamins A, C, and D, including where these vitamins are found in the diet and their roles in the body's metabolism. They will understand that these vitamins are not just nutritional components but are critical for maintaining health, supporting growth, and preventing diseases.
Summary of Lesson:
This lesson covers Vitamins A, C, and D, which are essential for various metabolic functions within the body. It will explore the rich food sources of these vitamins and their crucial roles in maintaining good health, including their involvement in vision, immune function, and bone health.
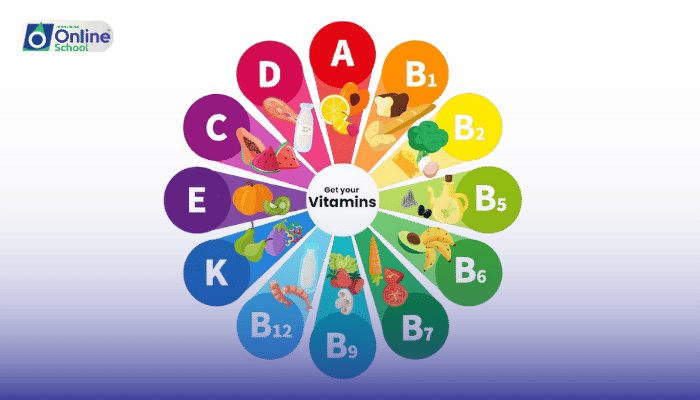
i. Vitamin A:
- Sources: Found in liver, fish oils, milk, eggs, and leafy green vegetables. Beta-carotene, found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and pumpkins, is converted into Vitamin A in the body.
- Metabolic Functions: Essential for good vision, especially in low light; important for cell growth and differentiation, and maintaining the health of the immune system and skin.
ii. Vitamin C:
- Sources: Rich sources include citrus fruits like oranges and lemons, strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli, and kiwifruit.
- Metabolic Functions: Vital for the synthesis of collagen, which is necessary for the repair and maintenance of skin, blood vessels, teeth, and bones; acts as an antioxidant; improves iron absorption; supports the immune system.
iii. Vitamin D:
- Sources: Obtained from sunlight exposure on the skin, fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks.
- Metabolic Functions: Critical for the absorption and regulation of calcium and phosphorus, ensuring healthy bone formation; plays a role in immune system function.
List of Important Questions for Self-Study:
i. Why is Vitamin A crucial for vision?
ii. How does Vitamin C contribute to wound healing and immune defense?
iii. What role does Vitamin D play in maintaining bone health?
iv. How can a deficiency in any of these vitamins affect the body?
v. What are some potential symptoms of vitamin excess or hypervitaminosis for Vitamins A, C, and D?
Important Terminologies Used in Lesson:
i. Vitamins: Organic compounds that are essential for normal growth and nutrition and are required in small quantities in the diet because they cannot be synthesized by the body.
ii.Collagen: The main structural protein found in skin and other connective tissues.
iii. Antioxidant: A substance that inhibits oxidation, especially one used to counteract the deterioration of stored food products or remove potentially damaging oxidizing agents in a living organism.
iv. Beta-carotene: A red-orange pigment found in plants and fruits, especially carrots and colorful vegetables, which the body converts into Vitamin A.